From the subtle alert in a smartphone to the powerful shaking of industrial machinery, a common technological principle is at work: the vibrating motor. This specialized device, engineered to convert rotational energy into oscillatory mechanical motion, is a fundamental component across a staggering array of applications. The versatility and reliability of the vibrating motor make it an indispensable, though often unnoticed, element in sectors ranging from consumer electronics and healthcare to construction, mining, and food processing.
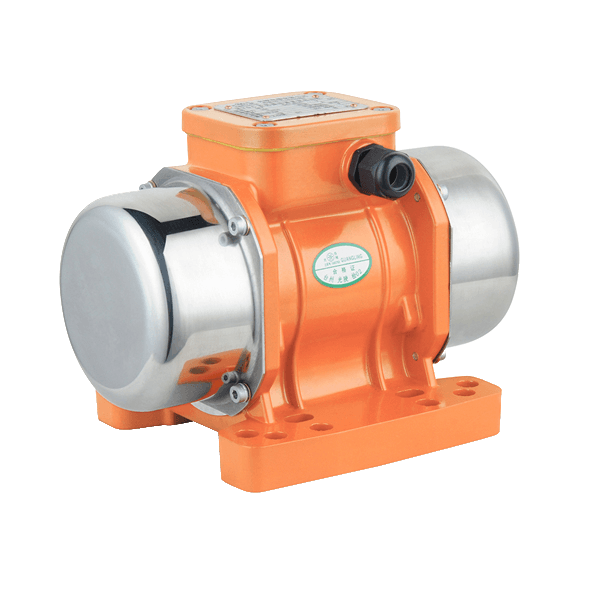
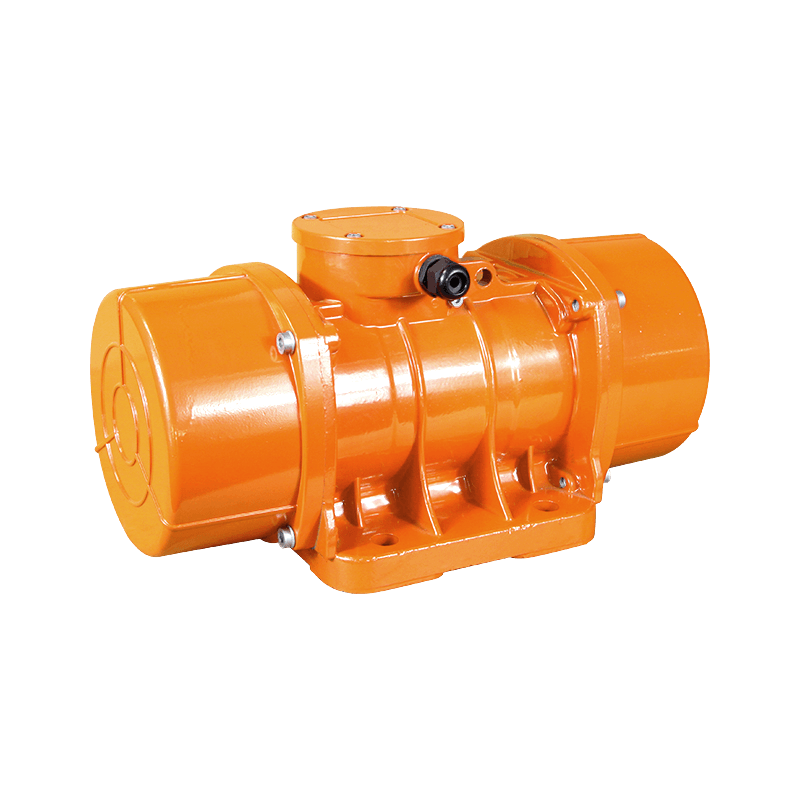
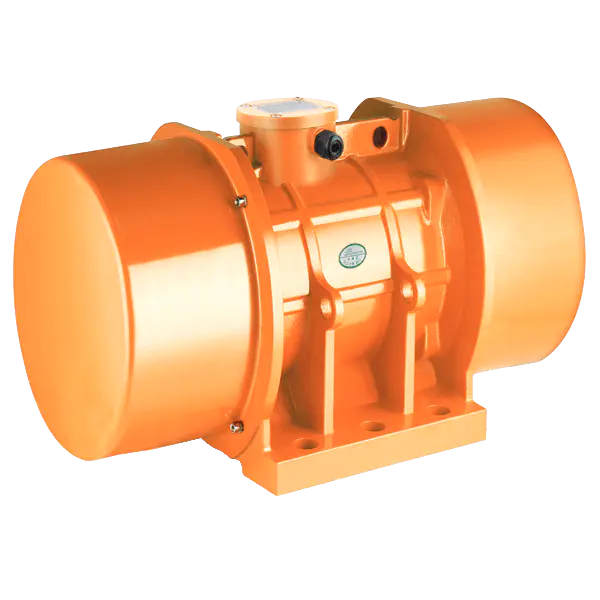
At its core, a vibrating motor operates on a simple but effective principle. It typically consists of a standard electric motor—either AC or DC—with an unbalanced mass, known as an eccentric weight, attached to its output shaft. As the motor spins, the offset weight generates a centrifugal force, causing the entire motor housing to vibrate. This vibration is then transmitted to the attached machine or device. The characteristics of this vibration—its frequency (speed) and amplitude (strength)—are precisely controlled by the motor's rotational speed and the mass and placement of the eccentric weight. This allows engineers to tailor a vibrating motor for tasks as delicate as haptic feedback or as robust as compacting tons of material.
The application spectrum of the vibrating motor is a testament to its adaptability. In the consumer realm, miniature vibrating motor units provide silent notifications in mobile phones, pagers, and wearables, and create immersive feedback in gaming controllers. They drive the oscillating heads of electric toothbrushes and facial cleansers. On an industrial scale, the vibrating motor is the workhorse of material handling. It powers vibratory feeders that meter bulk materials onto conveyor belts, drives screening and sorting machines that separate particles by size, and prevents material from clogging in hoppers and silos through constant agitation. In construction, specialized vibrating motor units are integral to concrete vibrators, ensuring the mix is dense and free of air pockets.
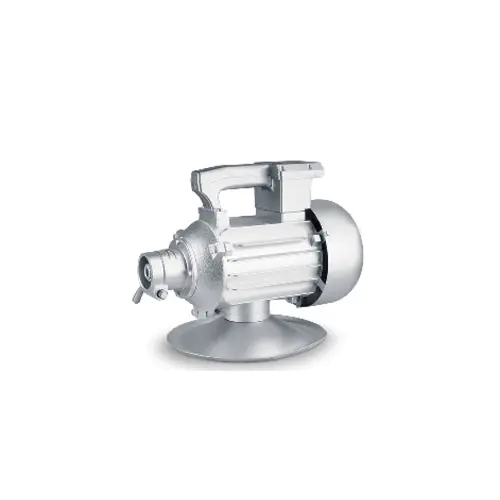

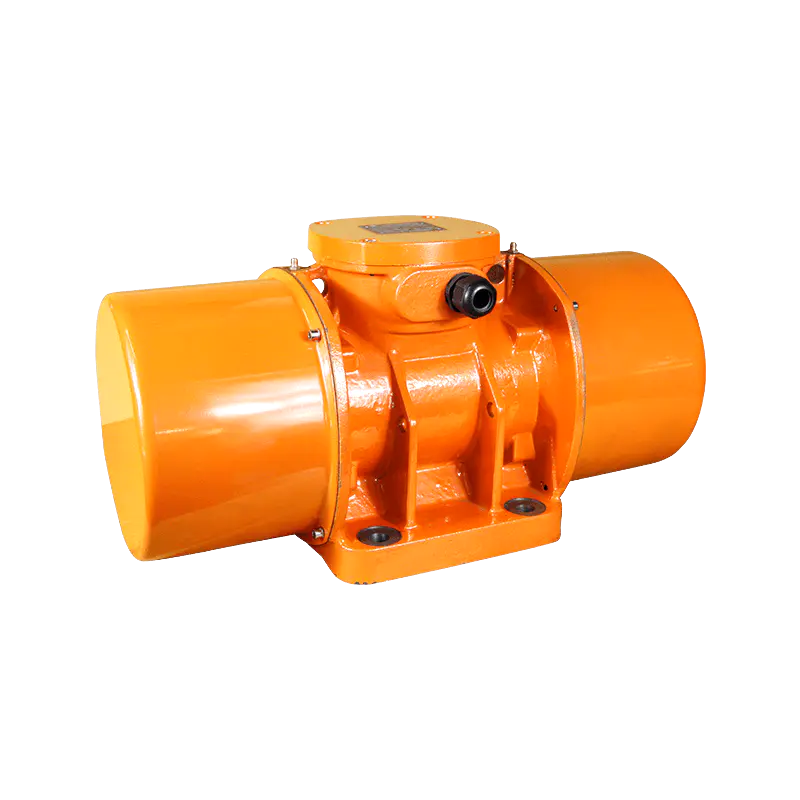
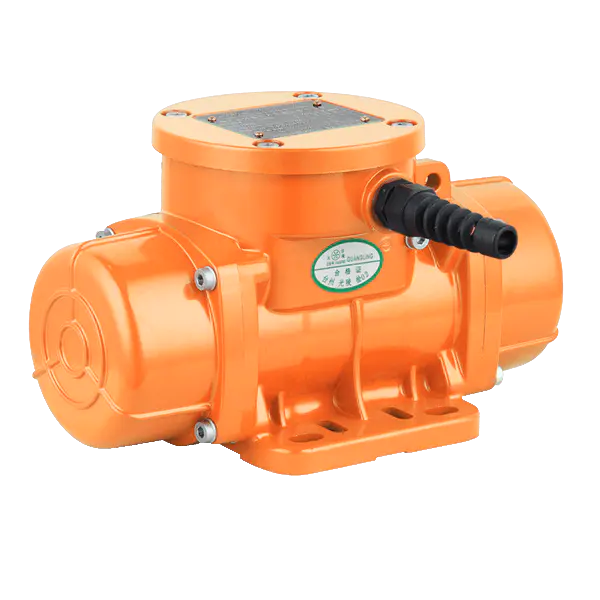
Design and construction are critical to the longevity and effectiveness of a vibrating motor. These units are subjected to constant internal stress from the unbalanced forces they create. Therefore, high-quality vibrating motor designs feature robust housings, often made of cast iron or hardened alloys, to contain the vibration and dissipate heat. Bearings are specifically selected to handle high radial loads, and sealing is paramount to protect internal components from environmental contaminants like dust, moisture, or, in food-grade applications, washdown procedures. This ruggedness ensures a vibrating motor can operate reliably for thousands of hours in demanding conditions.
Innovation in vibrating motor technology is focused on energy efficiency, smarter control, and enhanced durability. Trends include the development of more efficient electromagnetic designs to reduce power consumption, the integration of variable frequency drives for precise speed and amplitude control, and the use of advanced materials to extend service life. Furthermore, the integration of sensors for condition monitoring—tracking temperature, vibration signature, and bearing health—is paving the way for predictive maintenance, small unplanned downtime in industrial settings. As automation and the demand for precise material handling grow, the vibrating motor will continue to evolve, solidifying its role as a quiet, powerful, and essential driver of motion in both the devices we use every day and the industrial processes that build our world.

 英语
英语 葡萄牙语
葡萄牙语 西班牙语
西班牙语 русский
русский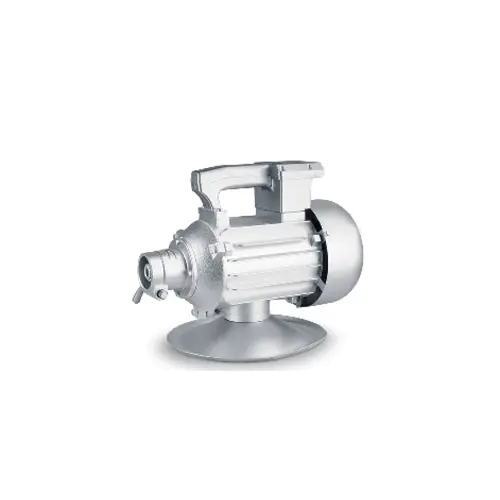




 Tel: + 86-576-86320988
Tel: + 86-576-86320988
 Fax: + 86-576-86333217
Fax: + 86-576-86333217
 E-mail:
E-mail:  Add: Dayangcheng Industrial Zone, daxi, wenling, zhejiang, china
Add: Dayangcheng Industrial Zone, daxi, wenling, zhejiang, china
