The compact yet critical component known as the vibration motor is experiencing a period of sustained development and broadening application. This electromechanical device, designed to convert electrical energy into oscillating motion, remains a fundamental feature in countless electronic products, from consumer gadgets to industrial tools. The ongoing innovation surrounding vibration motor technology focuses on enhancing efficiency, control, and miniaturization to meet the demands of increasingly sophisticated devices.
At its core, a vibration motor operates by generating a controlled, asymmetric force, typically through a small, off-balance weight attached to a rotating shaft. This simple but effective principle provides the tactile feedback users feel in smartphones and game controllers, as well as the alert function in pagers and wearables. The reliability and miniaturization of the vibration motor have been key to its pervasive use. Manufacturers continuously work to refine the internal components of a vibration motor to improve its lifespan, reduce power consumption, and allow for its integration into ever-smaller form factors without sacrificing performance.
The many recognizable application of the vibration motor is within the consumer electronics sector. Virtually every modern smartphone and tablet incorporates a small, precise vibration motor to provide silent notifications, haptic feedback for typing, and immersive effects in gaming and multimedia. In wearable technology, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches, a subtle vibration motor serves as a primary method for delivering alerts and reminders directly to the user. The quality and responsiveness of this vibration motor directly influence the perceived sophistication and user experience of the device, driving research into more nuanced and varied vibration patterns.
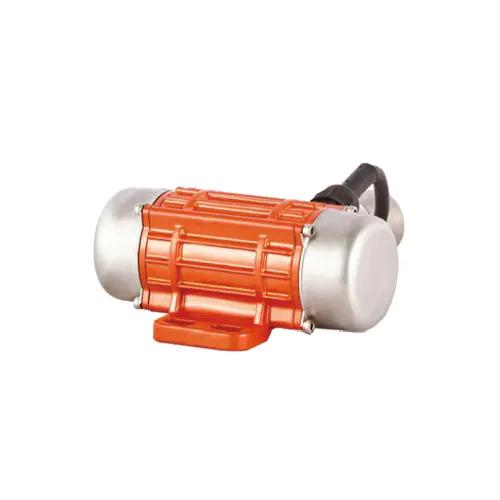

Beyond personal electronics, the utility of the vibration motor extends into several industrial and commercial domains. In medical devices, for instance, a compact vibration motor can be found in certain types of therapeutic massagers or alert systems for portable equipment. Automotive manufacturers integrate vibration motors into touchscreen interfaces and driver alert systems to provide tactile confirmation without requiring visual attention. Furthermore, industrial applications utilize robust vibration motors in equipment for sorting, compacting, and conveying materials, where their function is less about notification and more about imparting consistent mechanical motion.
Current research and development in vibration motor technology are oriented toward greater precision and programmability. There is a move away from simple on/off vibration toward more controlled, linear resonant actuator (LRA) types and other advanced haptic engines. These next-generation systems allow for the creation of more complex and realistic tactile sensations, simulating textures or specific click responses. This evolution of the vibration motor is crucial for developing more intuitive human-machine interfaces, especially in virtual and augmented reality systems where tactile feedback significantly enhances immersion.
The future trajectory for vibration motor technology appears intertwined with trends in automation, miniaturization, and interactive design. As the Internet of Things expands, small, efficient vibration motors may find new roles in providing discrete status alerts in smart home sensors or industrial monitoring equipment. Material science innovations could cause even smaller or more energy-dense designs. Ultimately, the vibration motor, though often hidden from view, will continue to be an essential component, translating digital signals into the physical world. Its ongoing refinement ensures it will remain a vital link between users and the technology they interact with daily, quietly enabling functionality across a diverse and growing range of applications.

 英语
英语 葡萄牙语
葡萄牙语 西班牙语
西班牙语 русский
русский




 Tel: + 86-576-86320988
Tel: + 86-576-86320988
 Fax: + 86-576-86333217
Fax: + 86-576-86333217
 E-mail:
E-mail:  Add: Dayangcheng Industrial Zone, daxi, wenling, zhejiang, china
Add: Dayangcheng Industrial Zone, daxi, wenling, zhejiang, china
